Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- allow_anonymouse
- datagridview 직접입력
- pm2
- mySQL_Replication
- AntDesign
- tailwind
- DataGridView 직접 입력
- mosquitto.conf
- 서버동기화
- setInterval 정지
- pm2 설치
- map이 undefined가 뜰 때
- pm2 시작
- mosquitto
- html #select #option #multiple
- invalid data
- setInterval 중지
- DatePicker
- vite
- pm2 확인
- 데이터테이블 데이터 넣기
- pm2 상태 확인
- react
- 1883
- c# datagridview 데이터 넣기
- setInterval clear
- 맥 어드레스
- setInterval 외부 정지
- listener 1883
- timepicker
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발 노트
c# 배열 본문
velog
velog.io
[배열]
배열은 같은 형식의 복수 인스턴스를 저장할 수 있는 형식
참조형식으로써 연속된 메모리 공간을 가리킨다.
[선언]
데이터형식[] 배열이름 = new 데이터형식[ 용량 ];
int[] scores = new int[5]; // 용량이 5개인 int형식의 배열
[데이터 저장]
배열이름[ 인덱스 ] = 값;
scores[0] = 80; // scores배열의 첫번째 값 저장 (인덱스 0부터 시작)
[배열 ^연산자] // ^연산자 : 컬렉션의 마지막부터 역순으로 인덱스를 지정하는 기능
// System.Index의 인스턴스 생성
System.Index last = ^1; // ^1 = 배열의 마지막을 나타내는 인덱스
scores[last] = 34; // scores[scores.Length-1] = 34;
// 더 간결한 버전
scores[^1] = 34; // scores[scores.Length-1] = 34;[배열 초기화]
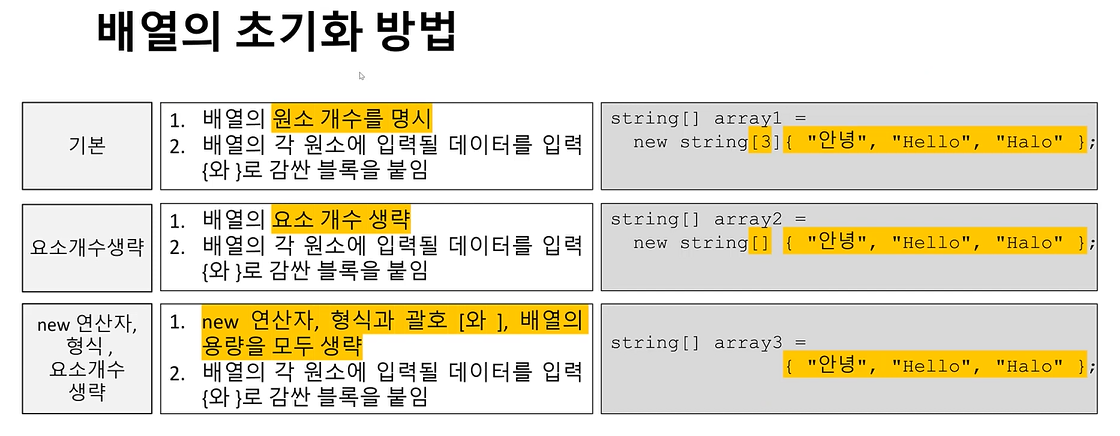
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 방법1 : 배열 형식, 용량/길이 명시
string[] array1 = new string[3] { "안녕", "Hello", "Halo" };
Console.WriteLine("array1...");
foreach (string greeting in array1)
Console.WriteLine($" {greeting}");
>array1...
>안녕
>Hello
>Halo
// 방법2 : 배열 형식만 명시 (용량/길이 생략)
string[] array2 = new string[] { "안녕", "Hello", "Halo" };
Console.WriteLine("\narray2...");
foreach (string greeting in array2)
Console.WriteLine($" {greeting}");
>array2...
>안녕
>Hello
>Halo
// 방법3 : 배열 형식, 용량/길이 모두 생략
string[] array3 = { "안녕", "Hello", "Halo" };
Console.WriteLine("\narray3...");
foreach (string greeting in array3)
Console.WriteLine($" {greeting}");
>array3...
>안녕
>Hello
>Halo
}[System.Array 클래스 주요 메소드, 프로퍼티]
<T>
형식 매개변수(Type Parameter)
T 대신 배열의 기반 자료형을 인수로 입력하면 컴파일러가 해당 형식에 맞춰 동작하도록 메소드를 컴파일함
private static bool CheckPassed(int score)
{
return score >= 60;
}
private static void Print(int value)
{
Console.Write($"{value} ");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 배열 선언
int[] scores = new int[]{80, 74, 81, 90, 34};
// foreach문
foreach (int score in scores)
Console.Write($"{score} ");
Console.WriteLine();
>80 74 81 90 34
// 정렬
Array.Sort(scores); //Sort함수로 자동 정렬
// 모든 요소에 동일한 작업 수행
Array.ForEach<int>(scores, new Action<int>(Print)); // <int> : 배열 기반 자료형
Console.WriteLine();
>34 74 80 81 90
// 차원 반환
Console.WriteLine($"Number of dimensions : {scores.Rank}");
>Number of dimensions : 1
// 이진 탐색
Console.WriteLine($"Binary Search : 81 is at " +
$"{Array.BinarySearch<int>(scores, 81)}");
>Binary Search : 81 is at 3
// 찾고자 하는 특정 데이터의 인덱스 반환
Console.WriteLine($"Linear Search : 90 is at " +
$"{Array.IndexOf(scores, 90)}"); // 5번째지만 인덱스라서 5 - 1
>Linear Search : 90 is at 4
// 모든 요소가 지정한 조건에 부합하는지 여부 반환
Console.WriteLine($"Everyone passed ? : " +
$"{Array.TrueForAll<int>(scores, CheckPassed)}");
// CheckPassed : TrueForAll 메소드는 배열과 함께 '조건을 검사하는 메소드'를 매개변수로 받음
>Everyone passed ? : False
// 지정 조건에 부합하는 첫 번째 요소의 인덱스 반환
int index = Array.FindIndex<int>(scores, (score) => score < 60);
// 람다식 : FindIndex 메소드는 `특정 조건에 부합하는 메소드`를 매개변수로 받음
// 데이터 저장 및 변경
scores[index] = 61;
// 모든 요소가 지정한 조건에 부합하는지 여부 반환
Console.WriteLine($"Everyone passed ? : " +
$"{Array.TrueForAll<int>(scores, CheckPassed)}");
>Everyone passed ? : True
// 지정한 차원의 길이 반환 (다차원 배열에서 유용하게 사용)
Console.WriteLine("Old length of scores : " +
$"{scores.GetLength(0)}");
> Old length of scores : 5
// 크기 재조정 : 배열 용량 10으로 재조정
Array.Resize<int>(ref scores, 10);
// 길이/용량 반환
Console.WriteLine($"New length of scores : {scores.Length}");
>New length of scores : 10
// 모든 요소에 동일한 작업 수행
Array.ForEach<int>(scores, new Action<int>(Print));
Console.WriteLine();
> 61 74 80 81 90 0 0 0 0 0
// 모든 요소 초기화
// 숫자 형식 → 0 | 논리 형식 → false | 참조 형식 → null
Array.Clear(scores, 3, 7); // 인덱스 3~7까지 초기화
Array.ForEach<int>(scores, new Action<int>(Print));
Console.WriteLine();
>61 74 80 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
// 분할 : 배열의 일부를 다른 곳에 복사
int[] sliced = new int[3];
Array.Copy(scores, 0, sliced, 0, 3);
Array.ForEach<int>(sliced, new Action<int>(Print));
Console.WriteLine();
>61 74 80[배열 분할]
..연산자를 활용해 시작 인덱스와 마지막 인덱스를 이용해 범위를 나타내는 방법
..연산자의 두번쨰 피연산자, 즉 마지막 인덱스는 배열 분할 결과에서 제외된다.
..처럼 시작과 마지막 인덱스를 모두 생략하면 배열 전체를 나타내는 System.Range 객체를 반환한다.
// 첫 번째(0) ~ 세 번째(2) 요소
int[] sliced3 = scores[..3];
// 두 번째(1) ~ 마지막 요소
int[] sliced4 = scores[1..];
// 전체
int[] sliced5 = scores[..];
//System.Index 객체를 이용할 수도 있다.
System.Index idx = ^1;
int[] sliced5 = scores[..idx];
int[] sliced6 = scores[..^1]; // ^연산자를 직접 입력하면 코드가 더 간결해짐[다차원 배열]
[다차원 배열]
차원이 둘 이상인 배열
선언 문법은 2차원 배열의 문법과 같다. 다만 차원이 늘어날수록 요소에 접근할 때
사용하는 인덱스의 수가 2개, 3개, 4개...의 식으로 늘어나는 점이 다르다.
3차원 배열 : 2차원 배열을 요소로 갖는 배열
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ,] array = new int[4, 3, 2]
{
{ {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6} },
{ {1, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 6} },
{ {6, 5}, {4, 3}, {2, 1} },
{ {6, 3}, {5, 2}, {4, 1} },
};
for (int i = 0; i < array.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write("{ ");
for (int k = 0; k < array.GetLength(2); k++)
{
Console.Write($"{array[i, j, k]} ");
}
Console.Write("} ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
{1 2} {3 4} {5 6}
{1 4} {2 5} {3 6}
{6 5} {4 3} {2 1}
{6 3} {5 2} {4 1}[가변 배열]
[가변 배열]
다양한 길이의 배열을 요소로 갖는 다차원 배열
들쭉날쭉한 배열
선언
데이터형식[][] 배열이름 = new 데이터형식[가변 배열의 용량][];
int[][] jagged = new int[3][];
가변 배열의 요소로 입력되는 배열은 그 길이가 모두 같을 필요가 없다.
int[][] jagged = new int[3][];
jagged[0] = new int[5] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // 5
jagged[1] = new int[] { 10, 20, 30 }; // 3
jagged[2] = new int[] { 100, 200 }; // 2
가변 배열도 선언과 동시에 초기화가 가능하다.
int[][] jagged2 = new int[2][] {
new int[] { 1000, 2000 },
new int[4] { 6, 7, 8, 9 } };'프로그래밍 > C#' 카테고리의 다른 글
| c# 클래스 (0) | 2024.02.05 |
|---|---|
| 알람 작업 (0) | 2024.01.31 |
| C# 기초 문법 정리 (0) | 2024.01.24 |
| C# 자료형 (0) | 2024.01.24 |
| 바이너리파일 공부하기 (0) | 2022.04.22 |

